Qualitative Research: 5 Things You Need to Know
Amirah Khan • 2023-04-18
Qualitative research is a powerful method for understanding rich, complex phenomena. This versatile research approach is made up of distinct processes and features that reflect the dynamic nature of real life. In this blog, we’ll explore a number of topics, including the difference between methods and approaches, how AI is changing the game, and an overview of qualitative data analysis.
Qualitative research aims to explore subjective human experiences using non-numerical data. It is the process of collecting, interpreting, and analysing descriptive data, such as text, images, videos, and audio recordings. This type of research allows us to examine people’s thoughts, feelings, behaviours, experiences, and attitudes. By examining the real world in this way, we can gain insight into important issues and problems and generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research goes beyond numbers to help us understand the ‘why’ and ‘how’ behind the dynamic, subjective, and evolving nature of real life.
Qualitative Research Question Examples
- How do students perceive the use of artificial intelligence in education?
- What social factors influence employees' decisions to work from home?
- How can a mobile app feature be improved for better accessibility?
- What are customers' perceptions of a product's branding and visual identity?
- Why are young adults interested in starting their own businesses?
- What does diversity and inclusion mean to different minority groups?
5 Things to Know About Qualitative Research
Distinct Features of Qualitative Research
Design that Develops
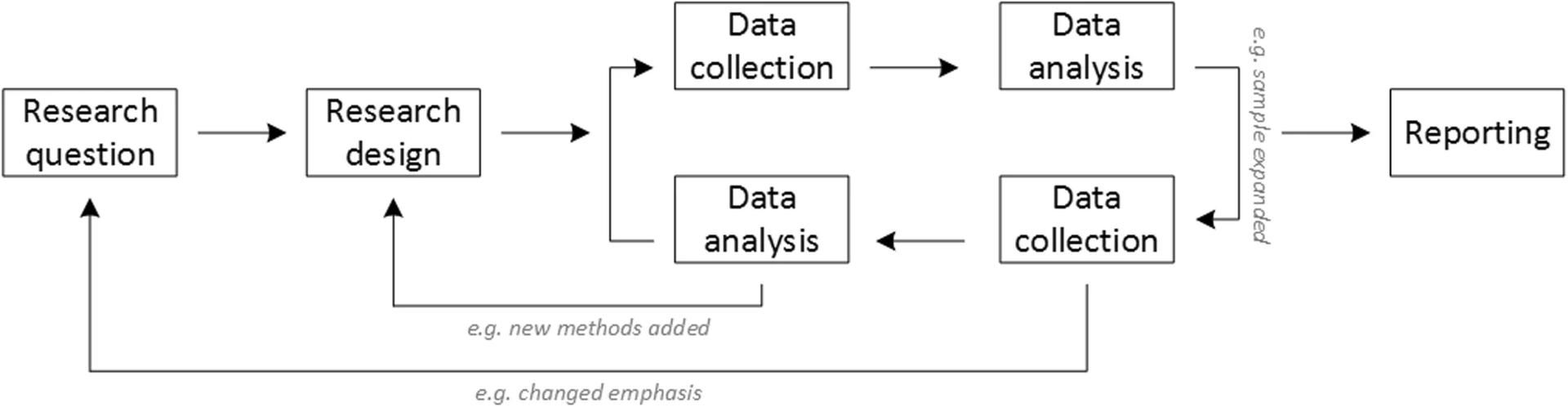
Qualitative research studies are described as having a flexible and emergent design. Researchers can adapt their study design to reflect new patterns, ideas, and insights that emerge from their data collection. Instead of being restricted by predefined theories or structures, qualitative research is able to reflect the evolving and dynamic nature of the real world. Researchers can explore the complexity and subjectivity of people using the data-driven and iterative approach of qualitative research. In this way, the design of a study develops or emerges from the research process.
[Source: How to use and assess qualitative research methods]
Researchers are Instruments
Qualitative researchers are considered to be key instruments in the research process. Their personal characteristics, beliefs, experiences, or biases can influence data collection and analysis. This makes them an integral part of qualitative research. For this reason, it’s important for researchers to reflect on, document, and justify their research process and decisions thoroughly. However, this communicative and personal approach can help researchers to build trust with participants. Through these interactions, people may offer interesting insights that explore the complexities and subtleties of the topic at hand.
Qualitative and Quantitative Research
In some cases, it can be beneficial to take a mix-methods approach that uses both qualitative and quantitative research. For market research, this can be particularly useful when a business still needs that empirical, large-scale data. Both qualitative and quantitative research be used in a complementary way to:
- Create hypotheses: Qualitative research findings can be further tested and proven using quantitative data. This can make quantitative research more relevant to the problem, topic, or issue being explored.
- Validate findings: On the other hand, qualitative research can be used to examine quantitative researching findings. This can help to explore the reasons behind the trends, relationships, or behaviours found in the numerical data, which can enhance understanding.
- Get a full picture: Qualitative research is often limited to smaller samples of people. However, this is important for getting that rich, exploratory data. Quantitative research can be used to provide a full picture by accessing a larger sample to confirm the findings. Or vice versa, quantitative results can be validated with a smaller subset of people.
Research Methods Vs. Approaches
In qualitative research, there are research methods and research approaches. Research methods are the tools used for data collection. In contrast, a research approach is the strategy that will be used to address the research question. This will often determine which research methods, also known as data collection tools, will be used to reach the research project’s goals.
There are five common qualitative research methods:
- In-depth interviews: One-to-one conversation where the researcher asks open-ended questions.
- Focus groups: Open-ended group discussion that is facilitated by the researcher.
- Observations: Researchers observe a natural setting and record detailed field notes.
- Surveys: Questionnaires with a range of open-ended questions.
- Secondary data: Existing data, such documents, photos, videos, audio interviews, and more are collected as data.
There are also five research approaches that influence which research methods are used:
- Grounded Theory: Using descriptive data, like observation field notes or interview transcripts, to develop theories in a bottom-up approach.
- Ethnography: Using immersion to understand the cultures, behaviour, and norms that exist within various groups.
- Phenomenological Research: Using lived experiences of people to understand a specific phenomenon or event.
- Narrative Research: Using the way people tell and construct stories to understand how they perceive their own experiences.
- Case Studies: Using informative stories to examine the process behind particular experiences. For example, a patient’s journey with treatment or a customer’s success story of a product.
Interpreting Qualitative Data
Qualitative data analysis is inductive and interpretive. This means that researchers aim to draw patterns from their rich, detailed data set, and make sense of the subjective meanings within the data. However, these interpretations are constructed using specific techniques or approaches. This is an important part of qualitative data analysis. Due to the subjective nature of qualitative data, it’s essential that the interpretation process, including the techniques used, are thoroughly documented and justified to give the findings some credibility.
These are the five common steps used to analyse qualitative data:
- Familiarise: Researchers need to immerse themselves into the data to begin noting down initial ideas. This could be during the process of managing the data, such as transcribing interviews or organising field notes.
- Code: The data can be broken down using ‘codes’ to begin labelling specific themes or topics. Researchers might summarise sections or interpret parts of the data as significant here.
- Categorise: These codes are then further organised into broader themes and categories, such as similar topics or ideas that were found in the data.
- Review: Researchers can refine the themes with clearer definitions and improve the structure of ‘story’ that the data analysis tells.
- Interpret: Finally, the findings need to be interpreted in the context of the research question. Researchers draw conclusions here and need to consider how their own personal involvement could have influenced the findings.
Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques:
- Textual Analysis: Explores the features of text, such as structure, language, content, and symbolism to understand meaning.
- Context Analysis Quantifies and categories common words, phrases, themes, subjects, and concepts.
- Thematic Analysis: Summarises data into smaller sections by identifying, interpreting, and analysing themes.
- Discourse Analysis: Examines the contextual meaning of language and how it relates to the topic at hand.
Revolutionising Qualitative Research with AI
Qualitative research is known to be labour intensive and time-consuming. Digital tools for transcription have made some of the qualitative research process easier. However, researchers are still left with large data sets to check, edit, explore and analyse. Artificial intelligence is now changing and revolutionising the world of research, qualitative research included.
For example, CoLoop is an AI-powered chat-style tool for researchers to explore their qualitative data. It’s like a powerful research assistant that can source the material you need. Simply upload your text, audio, or video research materials and begin asking questions. CoLoop can extract the quotes and insights you need, which saves you having to skim over transcripts several times. This AI tool is designed to help you complete reports and presentation decks with ease by allowing you to extract quotes and audio snippets with a click.
See More Posts
Cardy
Copyright © 2021 Govest, Inc. All rights reserved.